Grape root borer
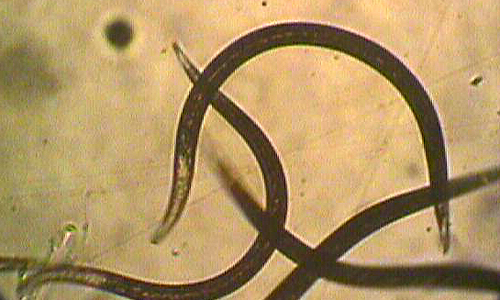
Damage caused by the Grape root borer
All the larval stages of grape root borer burrow into the grapevine roots and crown and feed internally. Severe internal feeding by these larvae can weaken and eventually kill the grapevines.
Facts (show all)
- Common names
-
- Grape root borer
- Scientific name
-
- Vitacea polistiformis
- Identification
-
Adults: Moths of grape root borer look like red paper wasps with dark brown forewings. They have clear hindwings with brown margins. Like wasps, they have also narrow yellow bands on the 2nd and 4th segments at the posterior region of the abdomen. These moths have orange to brown legs.
Eggs: Eggs of grape root borer are white in color.
Larvae: Mature larvae of grape root borer are white in color with brownish head capsule and about 25 mm long.
Pupae: Pupae of grape root borer are dark brown in color.
- Biology
-
Grape root borers overwinter as larvae inside the roots where resume feeding when temperature starts warming up. They remain inside the roots until they become mature. Matured larvae then leave roots and move in the soil for pupation. Adult moths emerge from the pupae from June through September. After mating, female moths lay eggs on the grape and weed leaves, and soil surface. These eggs hatch within a week into small larvae that fall off the leaves and burrow into the soil. These larvae then enter into grape roots where they make tunnels by feeding internally. They continue feeding inside the roots for over 20 months.
- Organic Control of the Grape root borer
-
- Following beneficial bugs are used for organic control of Grape root borer
- Beneficial Nematodes
-
- Heterorhabditis bacteriophora
- Steinernema feltiae
- Steinernema carpocapsae