Cutworms- The bronzed cutworm, Nephelodes minians
Damage caused by the bronzed cutworm
The bronzed cutworms are one of the the most important pests of turfgrass. Larvae of the bronzed cutworms generally feed at night on turf foliage. These larvae also cut off the stems of young seedlings of different crops near to the soil line. These cutworms generally cause most of the damage from May through June.
Facts (show all)
- Common names
-
- The bronzed cutworm
- Scientific name
-
- Nephelodes minians
- Identification
-
Adults: Adult moths of the bronzed cutworms have dark brown forewings and whitish gray hindwings.
Eggs: Eggs are round in shape and whitish to yellowish in color.
Larvae/Caterpillars: The bronzed cutworm larvae are dark gray to black in color with a dark bronzed- brown abdomen, dark brown head capsule, and three pale yellow colored stripes running along the entire body length. These larvae are about 1.5 inches long.
Pupae: Pupae are dark brown to black in color and spindle shaped.
- Biology
-
The bronzed cutworm overwinter as eggs. Eggs hatch in early spring into small larvae that continuously feed on turfgrass leaves and roots until they become mature in late May. These matured larvae then pupate in the soil. Adult moths emerge from pupae in late August through September and lay eggs. These eggs overwinter and life cycle continues. The bronzed cutworms generally complete one generation in a year.
- Organic Control of the bronzed cutworm
-
- Following beneficial bugs and plant products are used for organic control of the bronzed cutworm
- Egg parasitic wasps
-
- Trichogramma brassicae
- Trichogramma pretiosum
- Trichogramma minutum
- Trichogramma platneri
- Beneficial entomopathogenic nematodes
-
- Steinernema carpocapsae
- Steinernema feltiae
- Heterorhabditis bacteriophora
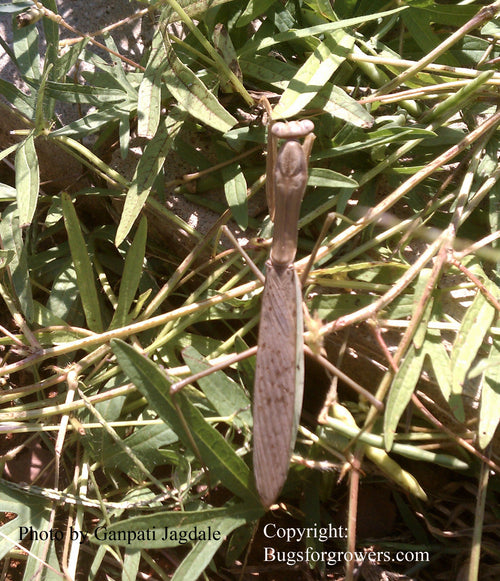
- Predatory praying mantis
-
- Tenodera aridifolia sinensis
- Stagmomantis crolina
- Plant Product
-
- Molt-X® - (Active ingredient – Azadirachtin a compound isolated from neem leaves)