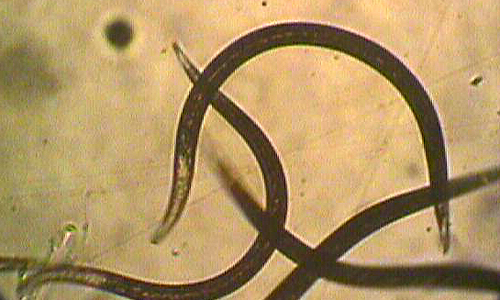
Green June Beetles
Damage caused by the Green June Beetles
Adults are the most damaging stage of green June beetles that mainly feed on different overripe fruits such as apples, blackberries, grapes, nectarine, peaches, pear, plum, prune and raspberry. In case severe infestation, several beetles can attack and enter into a single big ripe fruit like pear or peach and feed on its flesh. Infested fruits are unmarketable. Although grubs of green June beetles feed mainly on organic matter, their tunneling activity can damage turfgrass root system in addition to their direct feeding on roots of turfgrass.
Facts (show all)
- Common names
-
- Green June Beetles
- Scientific name
-
- Cotinis nitida
- Identification
-
Adults: Green June Beetle adults are velvet green with brownish to yellowish body margins, oval shaped. They are about 1 inch long and 0.5 wide.
Eggs: White and spherical in shape.
Grubs: Whitish in color with brown head capsule and three pairs of thoracic short legs. Grubs are C- shaped, about 2 inches long and unlike other grubs they crawl on their backs with their eggs in the air.
Pupae: Pale creamy to greenish in color.
- Biology
-
Green June beetles usually take about one year to complete their egg-to-egg life cycle. These beetles overwinter as grubs in the soil. When temperature begins warming up in the spring, overwintering grubs become active and start feeding on turf grass as well as decaying organic matter. Grubs pupate in the soil in late April through May. Adult beetles will emerge from pupae within 2-3 weeks and leave the soil in June through August. These beetles will then feed on different kinds of fruits. After mating, females select a turfgrass growing site with high organic matter content and moist soil for egg laying. Eggs hatch within 2 weeks into small grubs that tunnel through the soil and feed on the organic matter as well as on the turf roots. These grubs continue feeding until they become mature and winter approaches.
- Organic Control of the Green June Beetle
-
- Following beneficial bugs and plant products are used for organic control of the Green June Beetle
- Beneficial Nematodes
-
- Heterorhabditis bacteriophora
- Heterorhabditis indica
- Steinernema carpocapsae
- Plant product from neem tree seeds
-
- Molt-X- Active ingradient is Azadirachtin